During the past years, we have also learned that some adverse effects, although rarely present, are more frequently associated with DES implantation, and might be linked to durable polymers......
EUCATAX: A Multicenter Randomized Comparison of Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent with Biodegradable Polymer and Glycocalix Coating vs. Bare Metal Stent
Alfredo E. Rodriguez
During the past years, we have also learned that some adverse effects, although rarely present, are more frequently associated with DES implantation, and might be linked to durable polymers, which were always present in the first DES designs. Biodegradable polymers have the advantage of inducing a reduced inflammatory response, allowing the immunosuppressive agent to be completely released and eluted after degradation of the polymer.
The purpose of the present phase IV randomized clinical trial was to compare the efficacy and safety of a new DES design with a dual coating lawyer, a biodegradable polymer and glycocalyx, versus a bare metal stent (BMS) design in a wide patient/lesion subset.
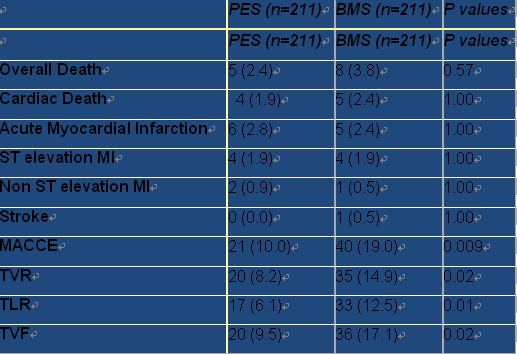
The first in man observational study with this technology has been previously conducted. From August 1st 2007 to August 31st 2009, from 2383 patients treated in the catheterization laboratories of the participant hospitals that were eligible for the study and met the inclusion criteria, 422 were randomized in the EUCATAX trial. 211 were included in PES with biodegradable polymer and glycocalyx coating and 211 in BMS arm. Cumulative clinical events at 17.3 ± 7.3 months was obtained in both groups. As we can see in Table, incidence of TVR was 8.2% in the PES versus 14.9% in the BMS group (P=0.02); TLR was 6.1% in the PES versus 12.5% in the BMS group (P=0.01). Incidence of TVF (9.5% vs 17.1% in the PES and BMS arms, respectively, P=0.02) and MACCE (10% vs 19% in the PES and BMS arms, respectively, P=0.009), which correspond to the major end points of the study, were also significantly improved in the eluted stent group .
Table. Clinical Outcome of eucaTAX Trial:Cumulative results at 17.3 months of follow up
At nine months, the rates of TVF (per protocol first end point) were 6.6% versus 14.7%
in the PES and BMS arms, respectively (P=0.024), and the rate of MACCE was 7.1% in the PES and 16.1% in the BMS group (P=0.016). Incidence of any ST was 1.4% in the PES and 1.9% in the BMS group;beyond one year, ST was non found in any group.
In the Figure we can observed survival freedom from TVF which indicate a significant improvement in the PES arm. Freedom from TVF was 90.5% in the PES versus 82.9% in the BMS arm, meaning a 44.5% reduction of this event (P=0.02).
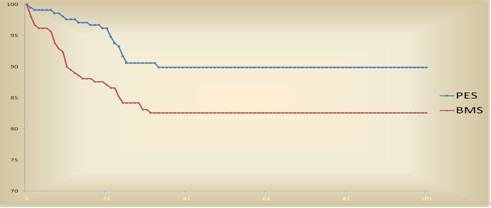
Figure. Survival curve from TVF:17.3 months of follow up from eucaTAX Trial
Finally presence of incomplete stent malapposition was more frequently seen in
the BMS arm: 9/37 (24.3%) versus 5/45 (11.1%) in the PES arm, respectively, (P=0.15). These differences were significantly in favor to the PES in proximal stent border (P=0.015). This unique IVUS finding was no reported previously with any DES technology.
In conclusion, at 17.3 months of follow up, patients treated with this novel DES technology had significant lower incidence of TVF and MACCE than those treated with a BMS design.



 京公网安备 11010502033353号
京公网安备 11010502033353号